
MDSAP’s Process-Based Audit Approach & Sequence
- Oriel STAT A MATRIX
- 0
- on Jul 21, 2017
Short-Term Pain = Long-Term Gain
The MDSAP audit model uses a process-based approach and defines the required audit sequence, nonconformity grading, scoring mechanism, and time requirements per process. In addition, the auditors must examine regulatory requirements from multiple countries. While the MDSAP audit may be more difficult at first, the payoff is big: A single audit satisfies multiple regulatory authorities.
MDSAPs Process-Based Audit Approach
MDSAP’s process-based approach is different from the traditional checklist-style audit that reviews documentation and conformance to standard requirements and procedures but it’s not new. FDAs QSIT (Quality Systems Inspection Technique) and effective auditing to the ISO 13485:2016 requirements also employ a process-based approach.
Auditors using a process-based approach assess the conformance of a process to regulatory requirements as well as the effectiveness of the process in producing the desired results. This approach not only reviews individual processes but also examines the interrelationships and connections between them, which allows organizations to understand both their level of conformance and the effectiveness of their quality management system (QMS).
During an MDSAP audit, the auditing organization (AO) will review procedures, map the process, and then ask auditees about the process to determine if their responses align with the procedure and if the process is effective in achieving desired results. The AO will analyze process performance against targets (e.g., nonconforming parts, product defects, product quality, and reliability targets) and planned results. They will also evaluate the handling of process/product nonconformities and effectiveness of the resulting corrective and preventive actions.Audit time for an MDSAP audit is based on tasks, not employee count, with an average of 15 minutes per task. This timed audit duration means that organizations need to articulate processes and interrelationships quickly and coherently.
The MDSAP Audit Sequence
When an AO performs an MDSAP audit, they follow a defined sequence. The purpose of the sequence is to provide a logical, efficient roadmap for the AO and ensure consistency across auditors.
The audit sequence contains four primary processes (Management; Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement; Design and Development; and Production and Service Controls), an enabling process (Purchasing), and two supporting processes (Device Marketing Authorization and Facility Registration, appearing in two spots below, and Medical Device Adverse Events and Advisory Notice Reporting). The primary processes are built on a foundation of risk management requirements.
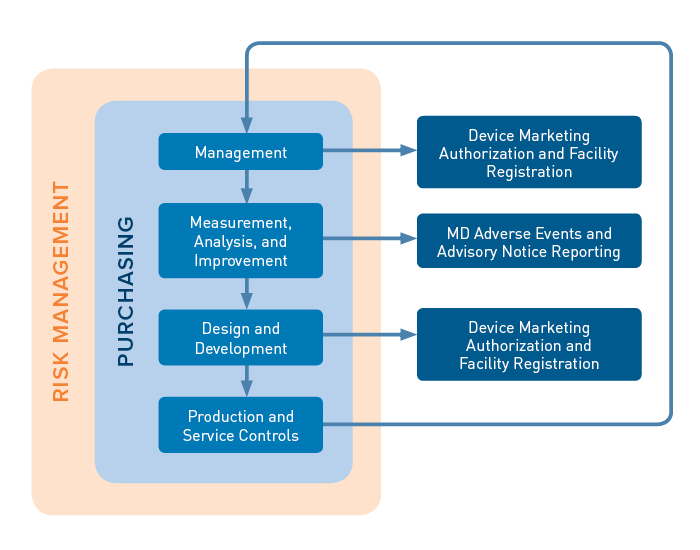
Each MDSAP process area includes audit objectives and a series of tasks that auditors use to determine compliance with ISO 13485 and the applicable regulatory requirements of the countries participating in the program (Australia, Brazil, Canada, Japan, and the US).
As the AOs navigate the audit sequence, they:
- Start and end each audit with the management process.
- Perform the audit tasks within each process area to determine if the process outcomes and purpose are achieved.
- Focus on linkages between processes (interrelationships).
- Assess risk control activities throughout the audit.
- Document nonconformities, paying special attention to the potential interrelationship of nonconformities.
The MDSAP Grading System
The MDSAP audit uses an established nonconformity grading system to standardize results across Auditing Organizations (AOs).
The MDSAP grading system(see: HTF/SG3/N19:2012 Nonconformity Grading System)does not use traditionalgrading criteriasuch as Major finding, Minor finding, and opportunity for improvement. Instead it assigns nonconformities a grade of 1 to 5 that is calculated using a grading matrix and escalation rules. If an AO finds two or more 4s or one or more 5+s, the AO has five days (MDSAP 5-Day Notice) to notify the appropriate Regulators (FDA, Brazil, etc.).
For more on MDSAP’s grading system, read our blog post:Ready, Set, Score!Understanding the MDSAP Grading System.
Preparing for a Process-Based Audit and the MDSAP Audit Sequence
Your internal audit team is the key to a successful MDSAP audit. They must be able to conduct process-based audits to prepare the organization to meet MDSAP requirements and practice for a successful AO audit.
Be sure to brief those with responsibility for the QMS at your organization on MDSAP, the MDSAP audit model, the audit sequence, and process-based auditing. The purpose of this briefing is to secure support to train your organizations internal auditors.
Remember that MDSAP is just one of several significant recent changes in the regulatory environment. Medical device manufacturers must also address the EU MDR and IVDR medical device regulations.
Oriel STAT A MATRIX offers a full suite of support options to ensure success with MDSAP including ourInternal Auditing to MDSAP class. Designed for experienced auditors, participants in this training learn how to apply MDSAP’s process-based audit approach and align your current internal audit program to the MDSAP requirements. You will also take a detailed look at country-specific requirements for the five MDSAP participant markets.


